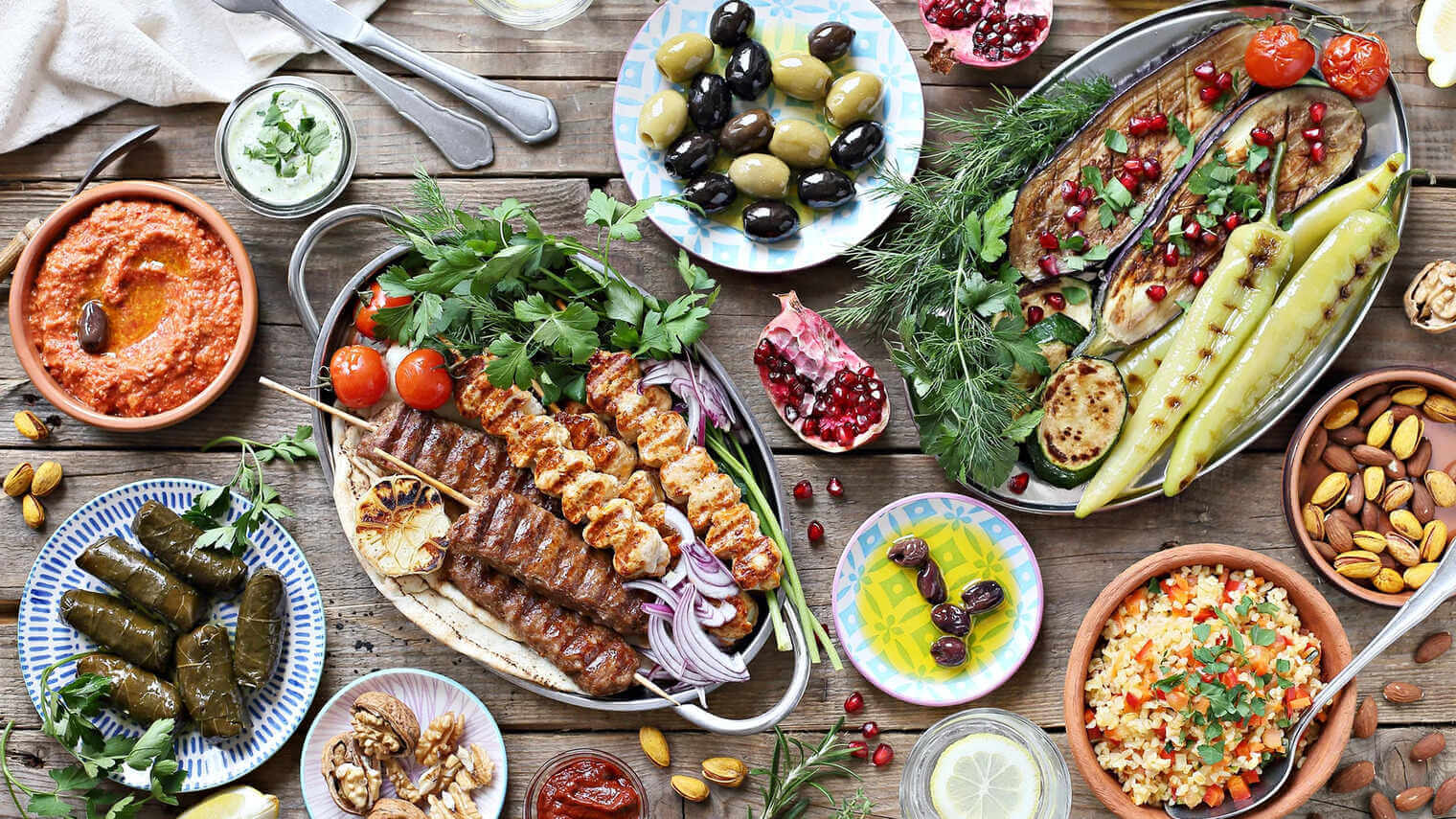

Mediterranean Cuisine: Healthy Recipes & Flavorful Secrets
What's in This Article
The Mediterranean region, with its sun-drenched coasts and rich cultural tapestry, offers a culinary experience that is both diverse and deeply rooted in tradition. Mediterranean cuisine is celebrated worldwide for its emphasis on fresh, seasonal ingredients and a variety of plant-based foods, which contribute to its health benefits and rich flavors. At the heart of this cuisine are core elements such as olive oil, wheat, and grapes, which are used to produce staples like olive oil, bread, pasta, and wine. Olive oil, often referred to as "liquid gold," is a fundamental ingredient in Mediterranean cooking, used for cooking, dressing salads, and dipping bread. Fresh herbs such as basil, oregano, rosemary, and thyme are generously used to add flavor to various dishes. Vegetables like tomatoes, aubergines, courgettes, peppers, and artichokes are central to Mediterranean dishes, appearing in soups, stews, roasts, and salads.
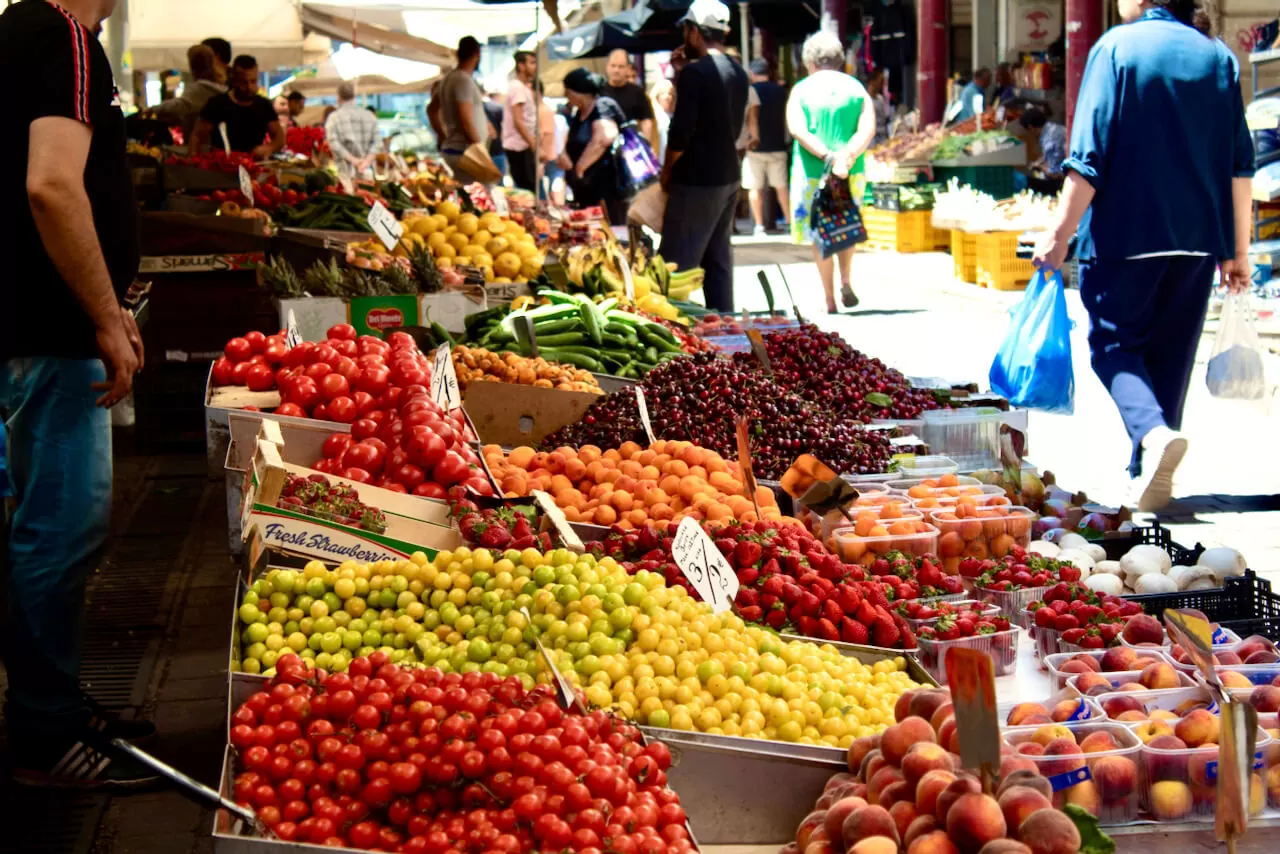

The Mediterranean region is famed for its vibrant local markets, where the abundance of fresh, seasonal ingredients reflects the essence of its celebrated cuisine.
The Historical Roots of Mediterranean Cuisine
The history of Mediterranean cuisine is as rich and diverse as the region itself. Spanning thousands of years, this culinary tradition has been shaped by the various cultures and civilizations that have inhabited the Mediterranean basin. From the ancient Greeks and Romans to the Ottomans and Moors, each culture has left its mark on the region's food, creating a tapestry of flavors and techniques that continue to evolve today.
Ancient Greek Influence
The ancient Greeks were among the first to cultivate the Mediterranean diet, emphasizing the use of olive oil, grains, and wine. Their diet was largely plant-based, with an abundance of fruits, vegetables, and legumes. The Greeks also introduced the concept of symposia, social gatherings centered around food and drink, which laid the foundation for the communal dining experiences that are still prevalent in Mediterranean culture today. For more insights into the ancient Greek diet, you can explore The Ancient Greek Diet.

The ancient Greeks were instrumental in shaping Mediterranean cuisine, introducing social dining traditions like the symposium, which celebrated food and community.
Roman Contributions
The Romans further developed Mediterranean cuisine by expanding agricultural practices and introducing new ingredients such as wheat, which became a staple in the form of bread and pasta. Roman feasts were elaborate affairs, showcasing a variety of meats, seafood, and vegetables, often seasoned with herbs and spices. The Roman Empire's vast trade networks also facilitated the exchange of culinary ideas and ingredients across the Mediterranean region.

The Romans significantly influenced Mediterranean cuisine, introducing new agricultural practices and ingredients, making feasting an integral part of their culture.
Arab and Moorish Influence
The Arab and Moorish invasions of the Iberian Peninsula brought a wealth of new ingredients and cooking techniques to Mediterranean cuisine. Spices such as saffron, cumin, and cinnamon became integral to the region's culinary repertoire, adding depth and complexity to dishes. The introduction of rice, sugar, and citrus fruits further enriched the Mediterranean diet, leading to the creation of iconic dishes like paella and couscous.
Ancient trade routes across the Mediterranean facilitated the exchange of ingredients and culinary practices, shaping the rich tapestry of the region's cuisine.
Key Ingredients of Mediterranean Cuisine
At the heart of Mediterranean cuisine are a few key ingredients that define its flavors and health benefits. These ingredients are not only staples in the region's diet but also contribute to its reputation as one of the healthiest diets in the world.
Olive Oil: The Liquid Gold
Olive oil is the cornerstone of Mediterranean cooking, used for everything from frying and sautéing to dressing salads and drizzling over finished dishes. Its rich, fruity flavor and high monounsaturated fat content make it a healthy choice for cooking and consumption. Extra virgin olive oil, in particular, is prized for its purity and robust flavor. For a comprehensive list of Mediterranean diet staples, including olive oil, check out A Complete Food List for The Mediterranean Diet.
Fresh Herbs and Spices
Fresh herbs such as basil, oregano, rosemary, and thyme are essential to Mediterranean cuisine, providing aromatic flavors that enhance the natural taste of ingredients. Spices like saffron, cumin, and paprika add warmth and complexity to dishes, reflecting the region's diverse cultural influences. These herbs and spices are often used in combination, creating layers of flavor that are both vibrant and harmonious.
Seasonal Vegetables and Fruits
Vegetables and fruits are central to Mediterranean cuisine, with an emphasis on fresh, seasonal produce. Tomatoes, aubergines, courgettes, peppers, and artichokes are commonly used in a variety of dishes, from salads and stews to roasts and gratins. Fruits such as figs, grapes, and citrus are enjoyed fresh or dried, adding natural sweetness to meals and desserts.
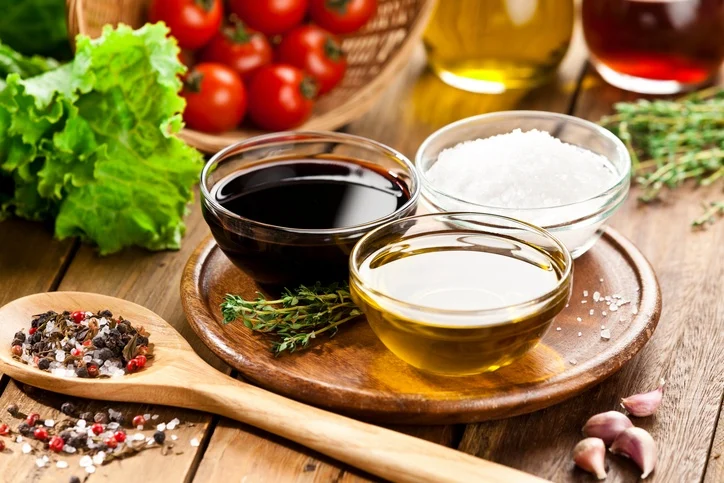

These key ingredients form the foundation of Mediterranean cuisine, celebrated for their robust flavors and health benefits.
Cooking Techniques in Mediterranean Cuisine
Mediterranean cuisine is characterized by a range of cooking techniques that highlight the natural flavors of ingredients while preserving their nutritional value. These techniques are often simple yet effective, allowing the quality of the ingredients to shine through.
Grilling and Roasting
Grilling and roasting are popular methods for cooking meats, seafood, and vegetables in Mediterranean cuisine. These techniques impart a smoky, charred flavor that enhances the taste of the ingredients. Grilled fish, roasted lamb, and charred vegetables are common dishes that showcase the region's love for these cooking methods. For a taste of Mediterranean-inspired grilling, try a Crispy Wood-Fired Thin Crust Pizza.
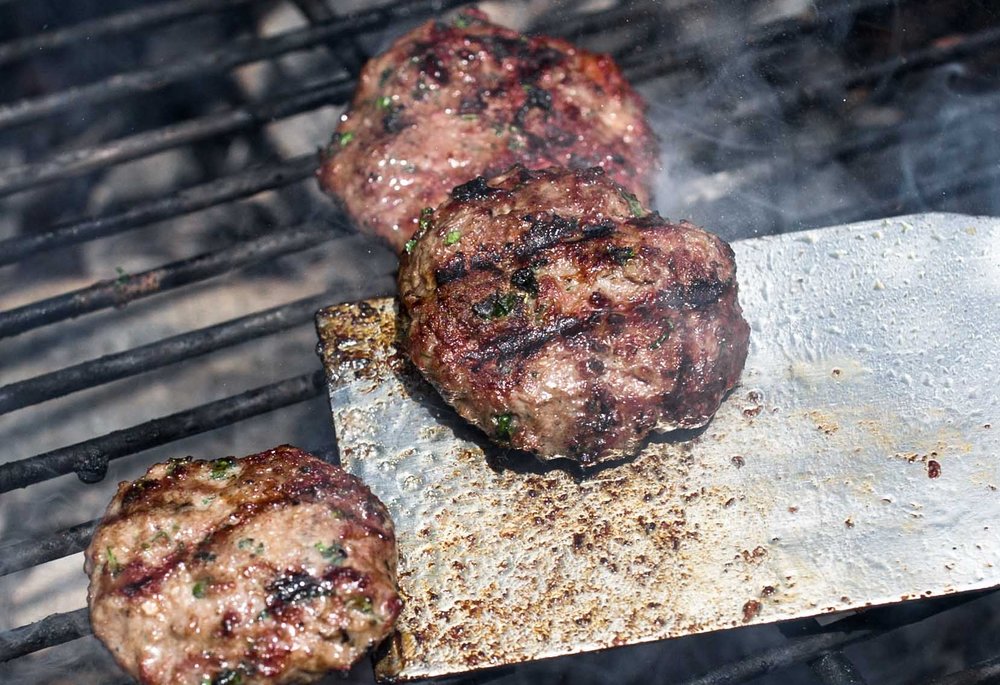

Grilling is a popular cooking technique in Mediterranean cuisine, imparting a distinct smoky flavor to a variety of meats, seafood, and vegetables.
Sautéing and Braising
Sautéing is a quick cooking method that involves frying ingredients in a small amount of oil, often with garlic and herbs, to create flavorful dishes. Braising, on the other hand, involves slow-cooking ingredients in a liquid, such as wine or broth, to develop rich, complex flavors. These techniques are commonly used for preparing stews, sauces, and vegetable dishes.
Baking and Steaming
Baking is a versatile cooking method used for preparing bread, pastries, and casseroles in Mediterranean cuisine. Dishes like Greek spanakopita and Italian lasagna are baked to perfection, with layers of flavor and texture. Steaming is another gentle cooking method that preserves the nutrients and natural flavors of ingredients, often used for preparing seafood and vegetables.
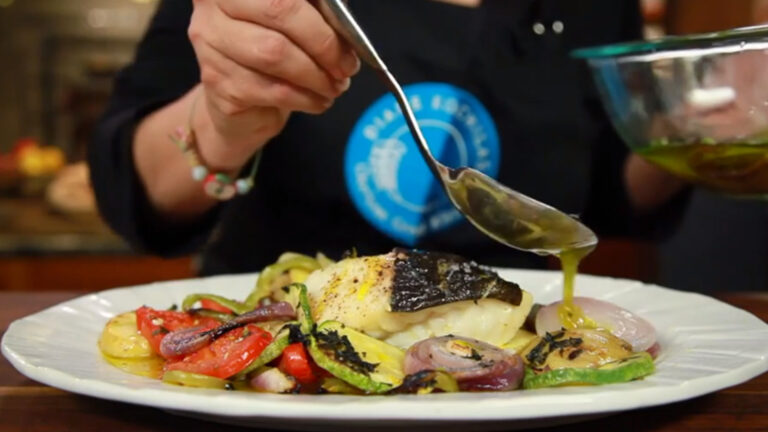

Traditional Mediterranean cooking techniques, like grilling and sautéing, enhance the natural flavors of ingredients while preserving their nutritional value.
The Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is renowned for its numerous health benefits, which have been extensively studied and documented. This diet emphasizes the consumption of whole, unprocessed foods, healthy fats, and a variety of plant-based ingredients, contributing to its reputation as one of the healthiest diets in the world.
Heart Health
The Mediterranean diet is associated with a reduced risk of heart disease, thanks to its emphasis on healthy fats, such as those found in olive oil, nuts, and fish. These fats help lower bad cholesterol levels and reduce inflammation, promoting cardiovascular health. The diet's high intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains also contributes to heart health by providing essential nutrients and antioxidants.
Weight Management
The Mediterranean diet encourages the consumption of nutrient-dense foods that are naturally low in calories, making it an effective approach for weight management. The diet's focus on whole grains, legumes, and vegetables provides a steady source of energy and promotes satiety, reducing the likelihood of overeating. Additionally, the diet's emphasis on healthy fats and lean proteins supports muscle maintenance and metabolic health.
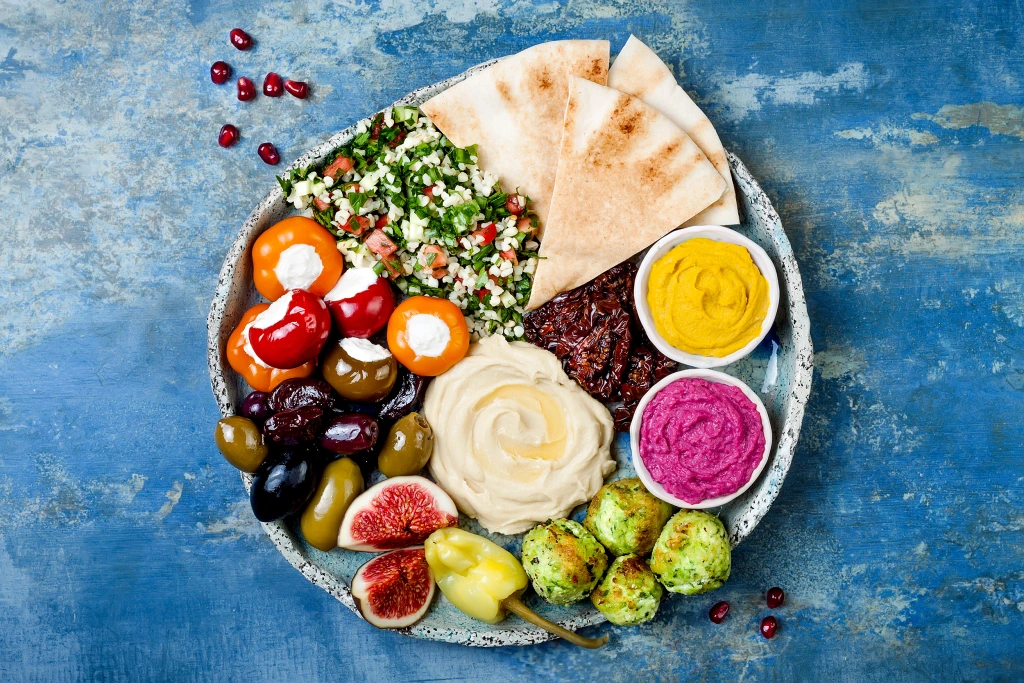

The Mediterranean diet focuses on nutrient-dense foods that aid in weight management by promoting satiety and providing sustained energy.
Longevity and Disease Prevention
Studies have shown that the Mediterranean diet is associated with increased longevity and a reduced risk of chronic diseases, such as diabetes, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders. The diet's rich array of antioxidants, anti-inflammatory compounds, and essential nutrients supports overall health and well-being, contributing to a longer, healthier life. For more information on the benefits of the Mediterranean diet, explore Do You Love Mediterranean Food?.
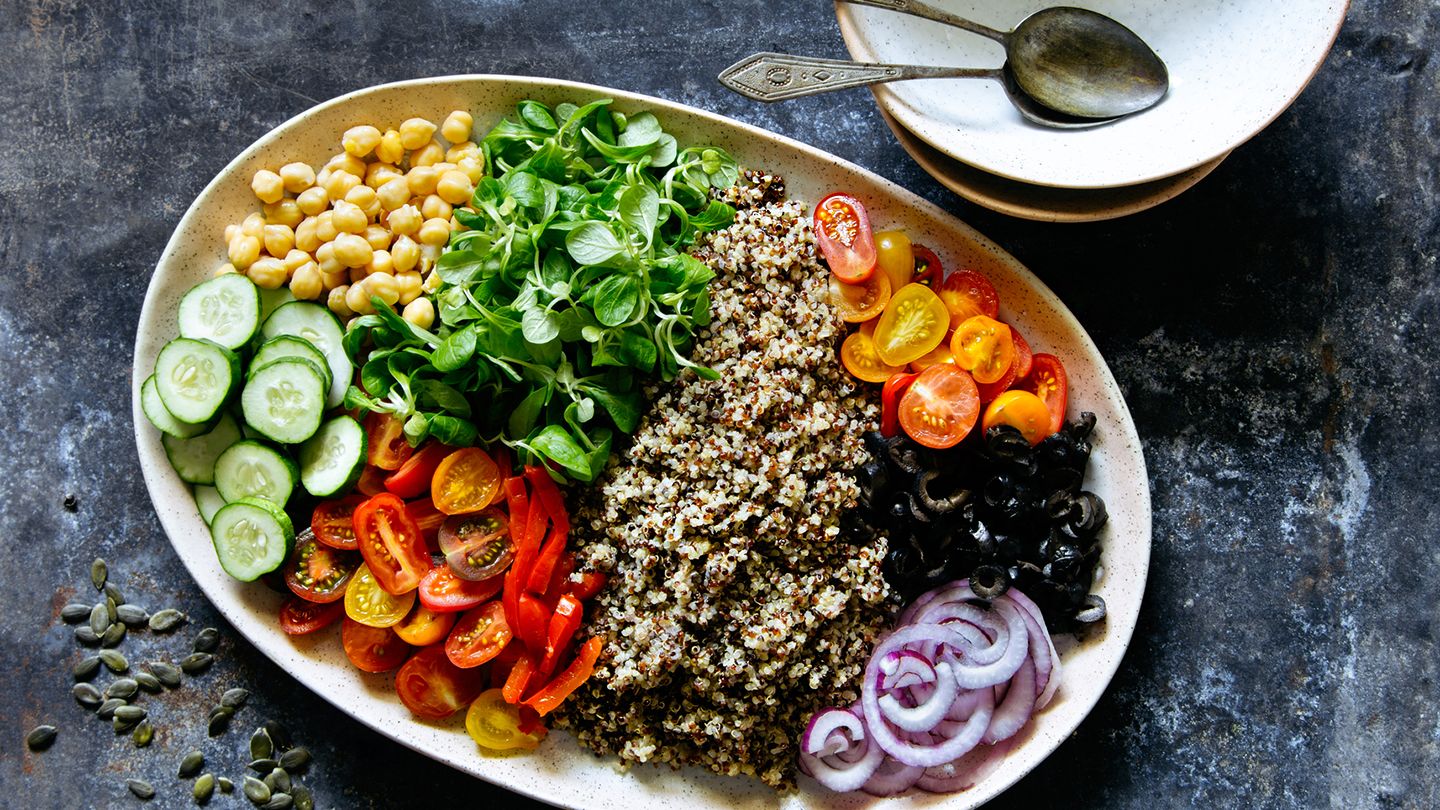

The Mediterranean diet is associated with increased longevity, as evidenced by the vibrant, healthy lifestyles of many Mediterranean communities.
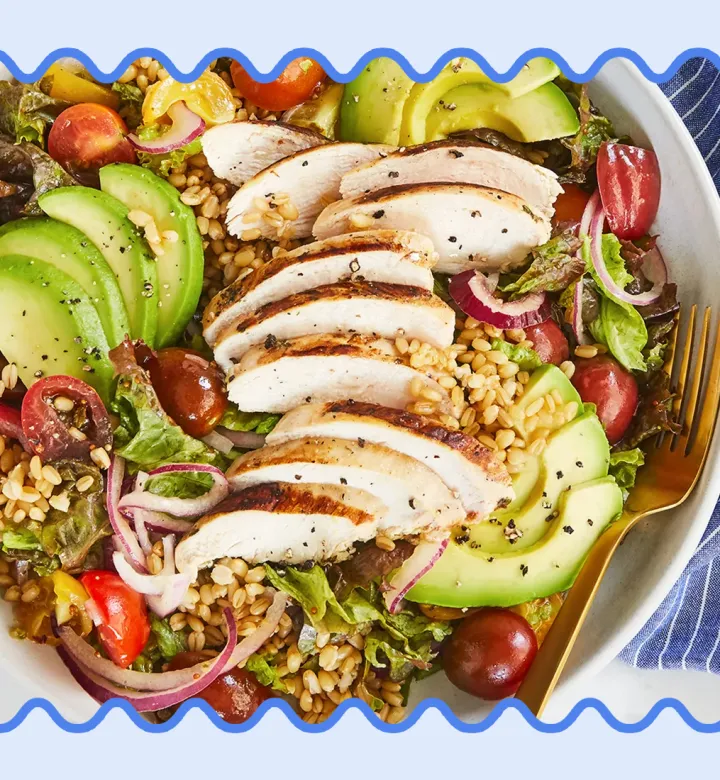

Extensive studies have documented the health benefits of the Mediterranean diet, linking it to lower risks of various chronic diseases and promoting longevity.
Iconic Mediterranean Dishes
Mediterranean cuisine is home to a wide variety of iconic dishes that showcase the region's diverse flavors and culinary traditions. These dishes are often characterized by their use of fresh, seasonal ingredients and aromatic herbs and spices.
Greek Moussaka
Greek moussaka is a classic Mediterranean dish that combines layers of eggplant, minced meat, and béchamel sauce, baked to perfection. This hearty casserole is seasoned with cinnamon, nutmeg, and oregano, creating a rich and comforting flavor profile. Moussaka is a testament to the Greek love for layered dishes and the use of aromatic spices.
Moroccan Tagine
Moroccan tagine is a slow-cooked stew that features a combination of meat, vegetables, and spices, cooked in a traditional earthenware pot. The dish is known for its complex flavors, achieved through the use of spices such as cumin, coriander, and saffron. Tagine is often served with couscous, a staple grain in North African cuisine, and is a perfect example of the region's rich culinary heritage.
Spanish Paella
Spanish paella is a vibrant rice dish that originated in the Valencia region of Spain. It is traditionally made with a variety of seafood, meats, and vegetables, cooked with saffron and other spices. Paella is a celebration of Spain's coastal bounty and is often enjoyed as a communal dish, shared among family and friends. For a refreshing drink to accompany your Mediterranean feast, try a Vibrant Tequila Sunrise.

Originating from Valencia, Spanish paella is a vibrant dish that encapsulates Spain's rich culinary heritage and coastal bounty.
Iconic Mediterranean dishes highlight the region's diverse flavors and culinary traditions, often featuring fresh, aromatic ingredients.
Conclusion
Mediterranean cuisine, with its rich history, diverse flavors, and health benefits, continues to captivate food enthusiasts around the world. Its emphasis on fresh, seasonal ingredients and plant-based foods makes it a sustainable and nutritious choice for those seeking a balanced diet. The Mediterranean diet, distinct from the cuisine, offers a wealth of health benefits, including reduced risk of heart disease, weight management, and increased longevity. Iconic dishes like Greek moussaka, Moroccan tagine, and Spanish paella showcase the region's culinary diversity and the unique flavors that define Mediterranean cooking.
As we explore the secrets of Mediterranean cuisine, we are reminded of the importance of tradition, community, and the simple pleasures of sharing a meal with loved ones. Whether you're savoring a plate of grilled vegetables, indulging in a slice of freshly baked bread, or enjoying a glass of wine, the Mediterranean way of eating offers a delicious and healthful approach to food that is both timeless and modern. For those looking to delve deeper into the world of Mediterranean cuisine, consider Exploring Mediterranean Cuisine for a comprehensive guide to the region's must-try staples.

The Mediterranean diet, known for its health benefits, emphasizes fresh, wholesome ingredients that contribute to a balanced and nutritious lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Mediterranean diet is primarily composed of whole, unprocessed foods that are rich in nutrients and healthy fats. Key components include:
- Fruits and vegetables: A variety of fresh, seasonal produce forms the foundation of the diet.
- Whole grains: Foods like whole wheat bread, pasta, and brown rice are staples.
- Healthy fats: Olive oil, nuts, and seeds provide essential fatty acids.
- Lean proteins: Fish, poultry, and legumes are preferred protein sources.
- Dairy: Consumed in moderation, often in the form of yogurt and cheese.
- Wine: Enjoyed in moderation, typically with meals.
The Mediterranean diet promotes heart health through its emphasis on healthy fats, such as those found in olive oil, nuts, and fish. These fats help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and reduce inflammation, which are key factors in maintaining cardiovascular health. Additionally, the diet's high intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients and antioxidants that support heart function and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Yes, the Mediterranean diet can aid in weight loss due to its focus on nutrient-dense, low-calorie foods. The diet encourages the consumption of whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, which provide a steady source of energy and promote satiety, reducing the likelihood of overeating. The inclusion of healthy fats and lean proteins supports muscle maintenance and metabolic health, further contributing to weight management.
Mediterranean cuisine employs a variety of cooking techniques that highlight the natural flavors of ingredients while preserving their nutritional value. Common techniques include:
- Grilling: Imparts a smoky, charred flavor to meats, seafood, and vegetables.
- Roasting: Enhances the taste of ingredients through caramelization.
- Sautéing: Quickly cooks ingredients in a small amount of oil, often with garlic and herbs.
- Braising: Slow-cooks ingredients in a liquid to develop rich, complex flavors.
- Baking: Used for preparing bread, pastries, and casseroles.
- Steaming: Preserves nutrients and natural flavors, often used for seafood and vegetables.
Mediterranean cuisine is home to a wide variety of iconic dishes that showcase the region's diverse flavors and culinary traditions. Some popular dishes include:
- Greek Moussaka: A layered casserole of eggplant, minced meat, and béchamel sauce.
- Moroccan Tagine: A slow-cooked stew of meat, vegetables, and spices.
- Spanish Paella: A vibrant rice dish with seafood, meats, and vegetables.
- Italian Caprese Salad: A simple salad of tomatoes, mozzarella, and basil.
- French Ratatouille: A vegetable stew with eggplant, zucchini, and peppers.
The Mediterranean diet differs from other diets in its emphasis on whole, unprocessed foods and healthy fats. Unlike restrictive diets that eliminate certain food groups, the Mediterranean diet encourages a balanced approach to eating, with a focus on plant-based ingredients, lean proteins, and moderate consumption of dairy and wine. This diet is sustainable and adaptable, making it a popular choice for those seeking a long-term, healthful way of eating.
Herbs and spices play a crucial role in Mediterranean cuisine, providing aromatic flavors that enhance the natural taste of ingredients. Fresh herbs such as basil, oregano, rosemary, and thyme are commonly used in a variety of dishes, from salads and sauces to roasted meats and vegetables. Spices like saffron, cumin, and paprika add warmth and complexity to dishes, reflecting the region's diverse cultural influences. These herbs and spices are often used in combination, creating layers of flavor that are both vibrant and harmonious.
Yes, the Mediterranean diet is well-suited for vegetarians, as it emphasizes plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains. Vegetarian-friendly dishes like Greek spanakopita, Italian caprese salad, and French ratatouille are staples of the cuisine. The diet's focus on healthy fats, such as those found in olive oil, nuts, and seeds, provides essential nutrients for vegetarians. Additionally, the inclusion of dairy products like yogurt and cheese offers additional sources of protein and calcium.